Time:
Comprehensive "Tokyo Shimbun" and Japan's TBS news website reported that recently, a rare "flesh-eating bacteria" caused by the disease spread in Japan. According to data, as of June 2, as many as 977 cases have been reported in Japan this year, breaking the previous record. --Global Times
Recently, a type of group A streptococcus bacteria known as "rare flesh-eating bacteria" has spread rapidly in Japan. The bacterium has caused a record number of infections in Japan, causing public panic, and Tokyo has issued its first epidemic alert for streptococcal infections. They are signs that we need to treat this seriously and scientifically.

Screenshot of a report by Fuji Shimbun, Japan
-What is " flesh-eating bacteria"?
In the case of Japanese infections, "flesh-eating bacteria" mainly refers to "virulent hemolytic streptococcal infections", which can also be called "outbreaks of A-hemolytic streptococcus".
-What is streptococcus?
Streptococci are a group of common gram-positive cocci within the group of streptococcus pyogenes, which are widely distributed in nature, in human and animal feces, and in the nasopharynx of healthy individuals.
-What is Group A Streptococcus?
Streptococci are categorized according to hemolytic reaction and group-specific antigens, etc. According to the different structure of antigens in the cell wall, they can be divided into A~H, K~V20 groups by serological methods. Group A Streptococcus (GAS) is responsible for about 90% of the human pathogenicity of streptococcal strains, while the other groups are less common.Group A Streptococcus has a strong invasive power and produces a variety of invasive enzymes and exotoxins. It is mainly transmitted through airborne droplets, skin and mucous membrane contact, and can also be transmitted through contaminated food.
It is reported that this "man-eating bacteria" can cause severe hemolytic streptococcal infection (streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, STSS), bacteria from the wound into the infected part of the necrosis, resulting in patients with multiple organ failure. The infection can be fatal within 48 hours, with a current mortality rate of 10-40%.
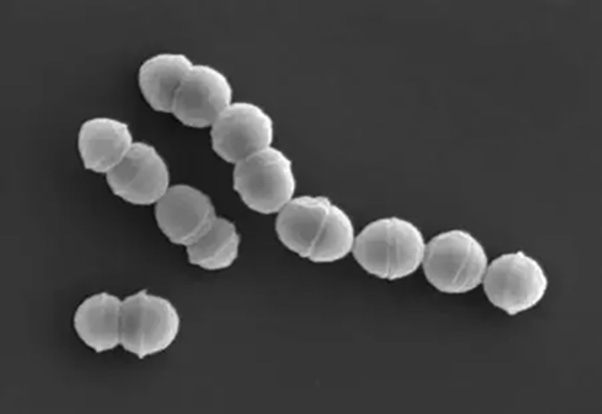
Structural diagram of hemolytic streptococci
"This strain was originally discovered in the United Kingdom, and is now triggering virulent-type infections in the U.S., Europe, Australia and elsewhere." --Professor, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital
"Most of the recent cases were not contracted through wounds, but through droplet transmission, possibly from a mutated strain of M1UK that is nine times more virulent than the original strain, which came from overseas. although the lethality rate is high, early medical attention can still lead to treatment." --Tokyo Infectious Disease Countermeasures Center expert
The source of the "flesh-eating bacteria" is not yet completely clear, but experts speculated that it may be related to a number of factors, including Japan's unique geographic and climatic conditions, the introduction of foreign bacteria due to globalization, and the mutation of bacterial resistance due to the misuse of antibiotics.
Patients infected with group A streptococcus, people with latent infections, and recovering carriers of that bacteria are the main sources of infection, and it is easy to see from the experts' statements that most of the recent "flesh-eating bacteria" infections in Japan have been spread by droplet transmission, and that patients with underlying illnesses, children, the elderly, and pregnant women are more susceptible to the infection.

Then we may ask, how to scientifically prevent the Japanese "flesh-eating bacteria"? You can pay attention to the following points:
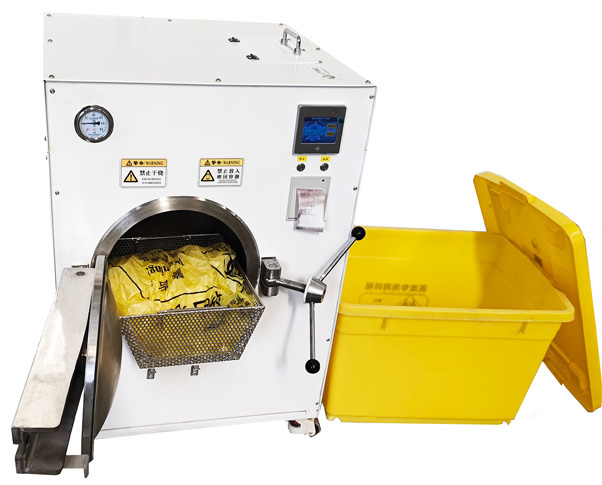

Li-Ying Equipment for the local disposal of medical waste
The safe handling of medical waste is particularly important in such large-scale bacterial infection events. Medical waste may contain infectious substances that, if not handled properly, can lead to secondary infections and environmental contamination.
Medical waste on-site disposal equipment is capable of efficient disinfection and sterilization using a combination of microwaves and high-temperature steam, which can flexibly help hospitals to safely handle medical waste, reduce environmental contamination, protect public health, and support the normal functioning of the healthcare system.
In conclusion, "flesh-eating bacteria" is a rare and dangerous bacteria that brings great threats to human health. We should actively prevent it, pay attention to medical waste disposal, reduce the risk of medical waste infection, and jointly tackle this challenge together!

What is the Polluter Pays…

Forests and wetlands are …

Of course! LI-YING has ex…
PDF Request